ABOUT GMDSS
GLOBAL MARITIME DISTRESS AND SAFETY SYSTEM
The Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) is an internationally agreed set of safety procedures, communication protocols, and equipment standards designed to enhance maritime safety and ensure rapid response in emergencies involving ships, boats, and even aircraft.
According to the International Maritime Organization (IMO), GMDSS provides a worldwide automated emergency communication network for ships at sea. Under SOLAS Convention Chapter IV, all passenger ships and cargo ships of 300 gross tonnage and above engaged on international voyages must carry GMDSS-compliant radio equipment.
Purpose of GMDSS
The primary goal of GMDSS is to eliminate unanswered distress calls and minimize delays in Search and Rescue (SAR) operations. It ensures that any emergency at sea results in an immediate and effective distress alert and response. GMDSS assures “... that any emergency at sea will result in a distress call and the response to that call will be immediate and effective” (IMO, Shipping Emergencies - Search and Rescue and the GMDSS, March 1999).
Modernized GMDSS – Key Updates
Following the 2024 modernization, GMDSS now supports modern communication technologies and removes obsolete systems. Key changes include:
· Use of Recognized Mobile Satellite Services (RMSS) instead of referencing specific providers like Inmarsat.
· Iridium and other Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite systems are now approved alongside traditional GEO systems.
· Removal of Narrow Band Direct Printing (NBDP) requirements for MF/HF.
· AIS-SART devices are now standard for SAR locating, replacing older radar-only SART.
· Enhanced EPIRBs with AIS and GNSS for improved location accuracy.
· Unified equipment requirements under SOLAS Chapter IV.
GMDSS Components
· Maritime Safety Information (MSI): Broadcasts navigational warnings, weather forecasts, and urgent safety messages via NAVTEX or satellite services.
· Digital Selective Calling (DSC): Automated distress alerting and calling on VHF, MF, and HF bands.
· EPIRB (Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon): Automatically transmits distress alerts via the COSPAS-SARSAT satellite system on 406 MHz, often with integrated GNSS and AIS.
· NAVTEX: Automated delivery of MSI in coastal areas.
· Search and Rescue Locating Devices:
- AIS-SART (preferred) or Radar SART for locating survival craft.
· Recognized Mobile Satellite Services (RMSS): Includes Inmarsat, Iridium, and future providers for global coverage.
· Ship Earth Station (SES): Provides continuous alerting in Sea Area A3 and beyond.
How it Works
In an emergency, GMDSS equipment automatically sends distress alerts with the vessel’s identity and position to Rescue Coordination Centers (RCCs) and nearby ships, ensuring rapid SAR response.
Danphone and GMDSS – Your Partner in Maritime Safety
At Danphone, we deliver advanced shore-based communication systems and test equipment to ensure compliance with international maritime safety standards and efficient port operations.
We help our customers with:
· Coastal Radio Communication Systems – Complete GMDSS-compliant solutions for VHF, MF/HF with DSC, NAVTEX, and AIS/VDES, including remote control and redundancy for 24/7 operation.
· Port Communication Systems – Integrated solutions for harbor authorities and VTS centers, enabling secure and efficient communication between vessels and port operations.
· Maritime Safety Information (MSI) Broadcast Systems – Reliable NAVTEX and AIS infrastructure for navigational warnings and weather forecasts.
· Futronic GMDSS Test Equipment – The industry-leading Futronic MKII tester for verifying radios, EPIRBs, AIS, NAVTEX, and SART devices, trusted by inspectors and service providers worldwide.
· Service, Support & Training – Expert assistance for installation, maintenance, and operator training to keep your systems compliant and operational.
With decades of experience in maritime communication technology, Danphone is your trusted partner for safe and efficient operations at sea and in port.
HOW TO CONDUCT A GMDSS INSPECTION
All communication and safety equipment on board vessels are required to undergo annual inspections such as GMDSS radio survey and VDR/SVDR annual performance testing (APT). These inspections should comply with SOLAS chapter IV, Functional Requirements of all communication and safety equipment onboard vessels.
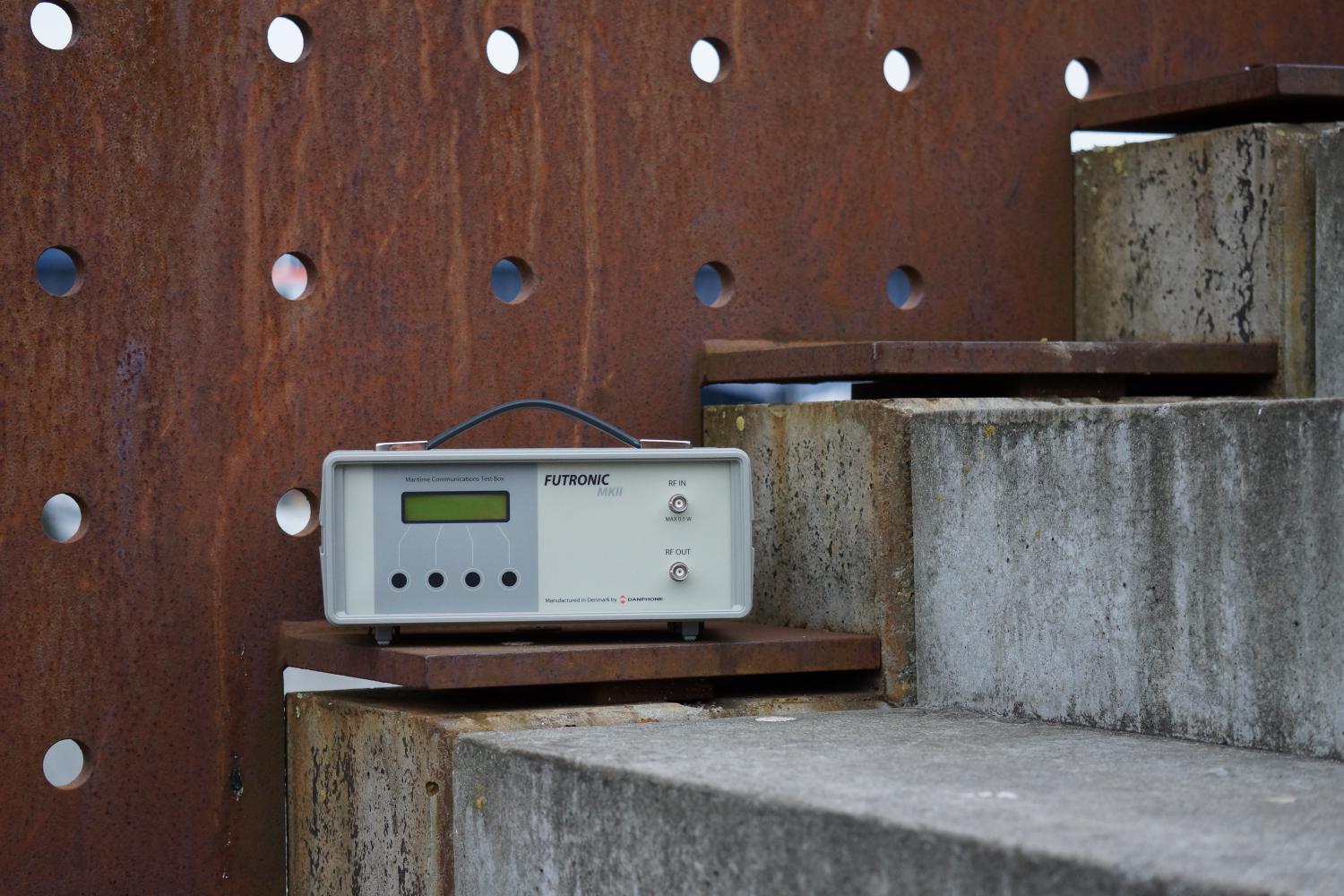
TEST EQUIPMENT FOR CONDUCTING RADIO INSPECTIONS: FUTRONIC MKII
Danphone’s Futronic test box for radio inspections is based on SOLAS Chapter IV requirements for radio equipment and capable of testing all regulated radio and safety equipment related to the GMDSS other than INMARSAT with approved self-test functionalities.
Futronic meets SOLAS Chapter IV, Functional Requirements, to the communications equipment onboard vessels by providing efficient and accurate testing on:

VHF radios
DSC data, ATIS, frequency, power, VSWR and deviation.
Measuring frequency and power simultaneously.
MF/HF radios
Measuring DSC data and frequency simultaneously.
NAVTEX receivers
Reception of transmitted NAVTEX messages.
AIS transponders
Measuring AIS data, frequency, power and VSWR simultaneously on:
- Class A & B transponders
- AIS base stations
- Aircraft Search and Rescue transponders
- Aids to Navigation devices (AtoN)
Search and rescue transponders
Measuring Data & frequency on:
- EPIRB
- Man Over Board (MoB) devices
- AIS SART beacon data & frequency
Furthermore, Futronic MKll complies with DNV’s regulations for test equipment (Service Suppliers Engaged in the Inspection and Testing of Radio Communication Equipment and Automatic Identification System on Vessels, March 2014; 2.9 Equipment and 2.11 Minimum required instruments).
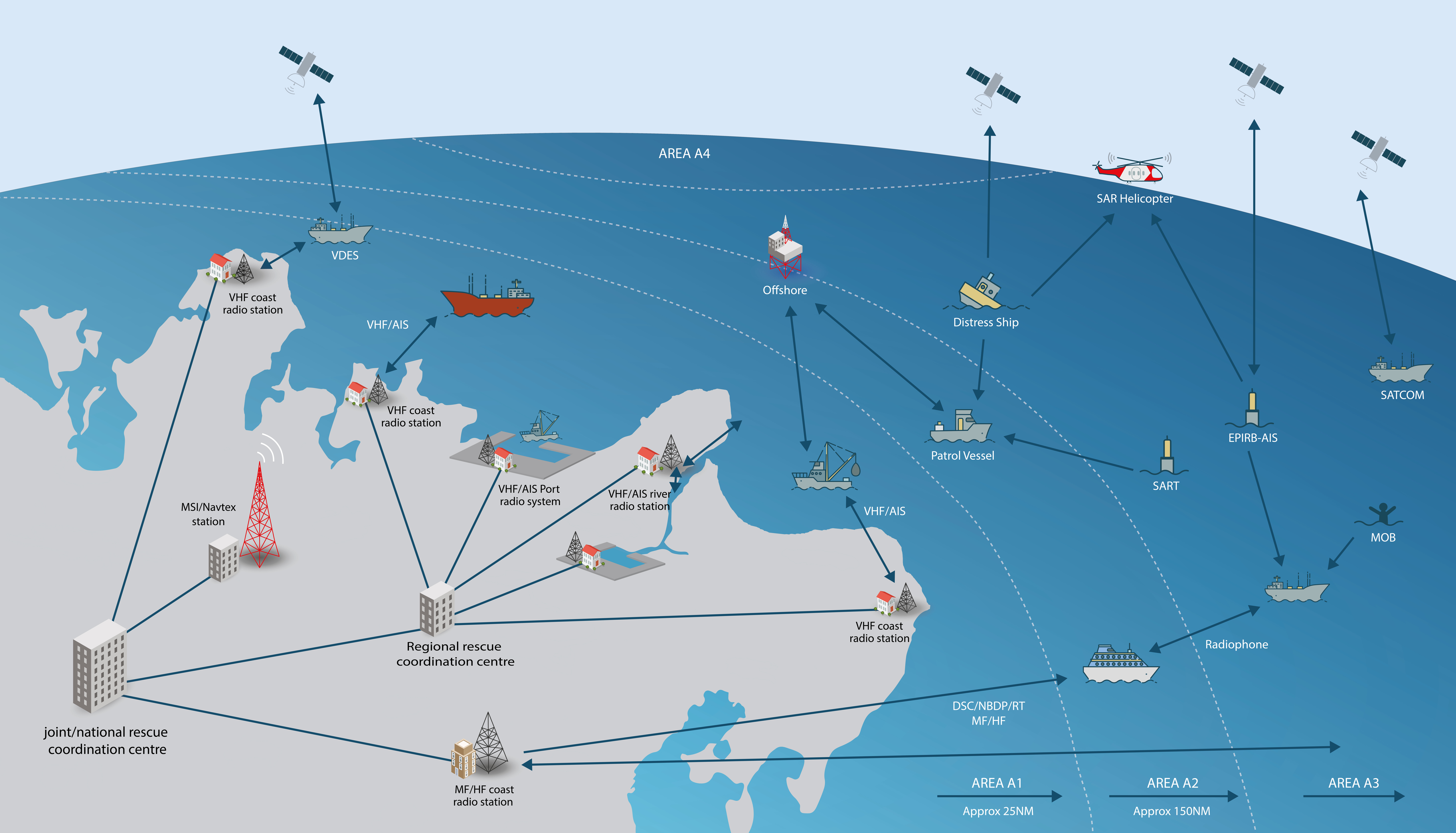
SEA AREAS
The GMDSS operates over 4 sea areas of coverage from shore to ship. The 4 sea areas are classified as: A1, A2, A3 and A4.
Sea area A1: Covered by VHF radio enabling Digital Selective Calling (DSC) and Radio Telephone (RT). Determined range of approximately 20-30 nautical miles.
Sea area A2: Covered by MF radio also enabling DSC and RT. Determined range up to 150 nautical miles.
Sea area A3: Covered by HF radio and Inmarsat geostationary satellite enabling DSC and satellite communication 70°N and below 70°S.
Sea area A4: Categorized as the polar regions above 70°N and below 70°S. This area requires HF radio with DSC.